As you exercise your blood flow to your muscles must increase. The increase in diastolic blood pressure on exercise in our group of healthy active men ranged from 12 to 16 mm hg at the lowest workload when heart rates ranged from 71 to 136 bpm.
 Why Doesn T Blood Pressure Increase During Exercise Quora
Why Doesn T Blood Pressure Increase During Exercise Quora
why does systolic pressure increase during exercise but not diastolic
why does systolic pressure increase during exercise but not diastolic is a summary of the best information with HD images sourced from all the most popular websites in the world. You can access all contents by clicking the download button. If want a higher resolution you can find it on Google Images.
Note: Copyright of all images in why does systolic pressure increase during exercise but not diastolic content depends on the source site. We hope you do not use it for commercial purposes.
Find primary care doctors near you.

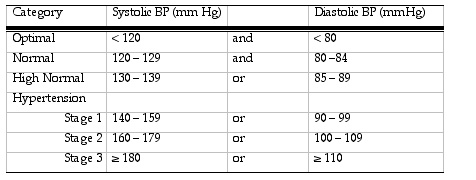
Why does systolic pressure increase during exercise but not diastolic. However some people experience abnormally low or high blood pressure during exercise and this requires medical assessment. Thus your systolic blood pressure increase during exercise is mainly a function of increased heart rate and contractilewhile the diastolic decrease or lack of increase is a function of a relaxation of the end vascular tension in the capillary and arteriole beds of the muscle groups working so hard. Contrariwise an increase in diastolic blood pressure of more than 10 mmhg during or after exercise represents an unstable form of hypertension and may be associated with coronary artery disease.
Why systolic blood pressure increase during exercise systolic pressure and exercese. You might be like me maintain good shape but still have heart disease. Not everyones diastolic blood pressure stays the same during exercise.
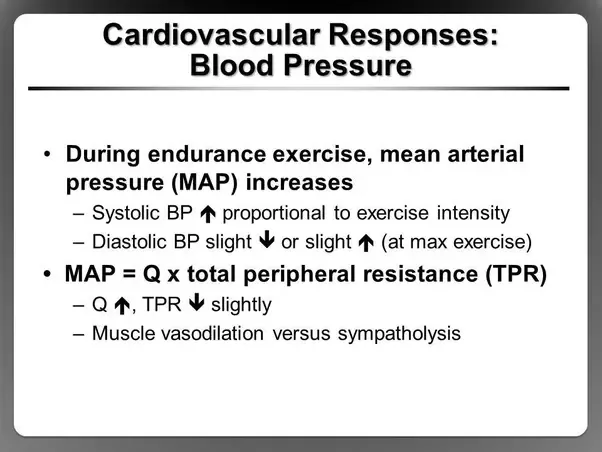
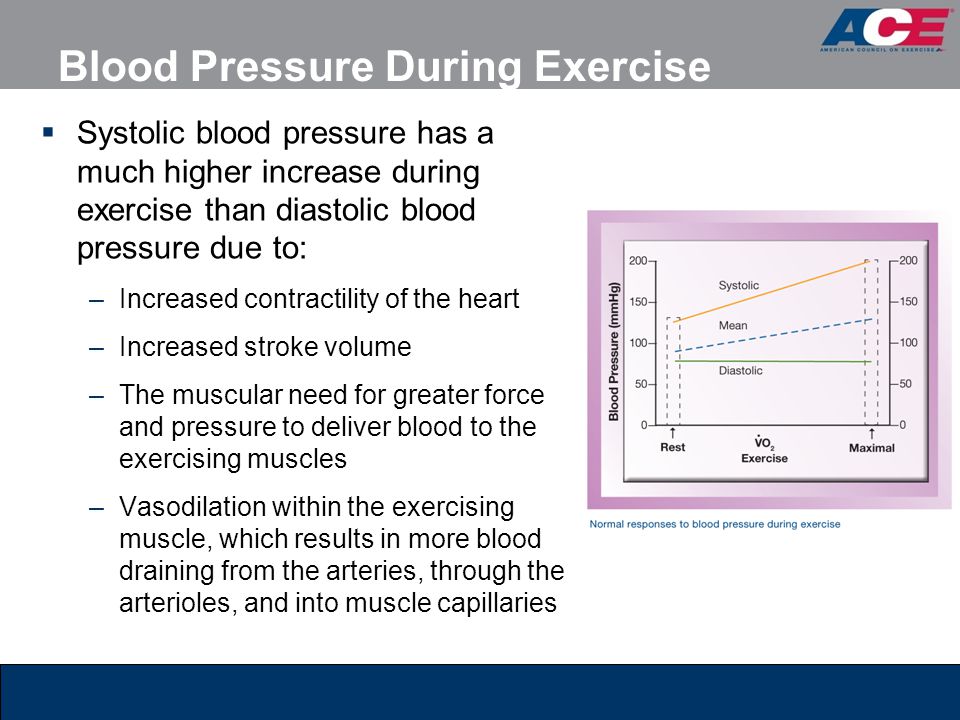
During aerobic exercise systolic pressure should gradually increase as your heart beats harder and faster and your arteries contract to pump more oxygen rich blood. However because the arteries in your working muscles start to dilate rather than constrict the net result is little change in your diastolic pressure. A dramatic increase in blood pressure during or after exercise could be a sign of.
This causes the heart to beat faster and harder. Blood pressure is simply the push of blood again. See a doctor who can help.
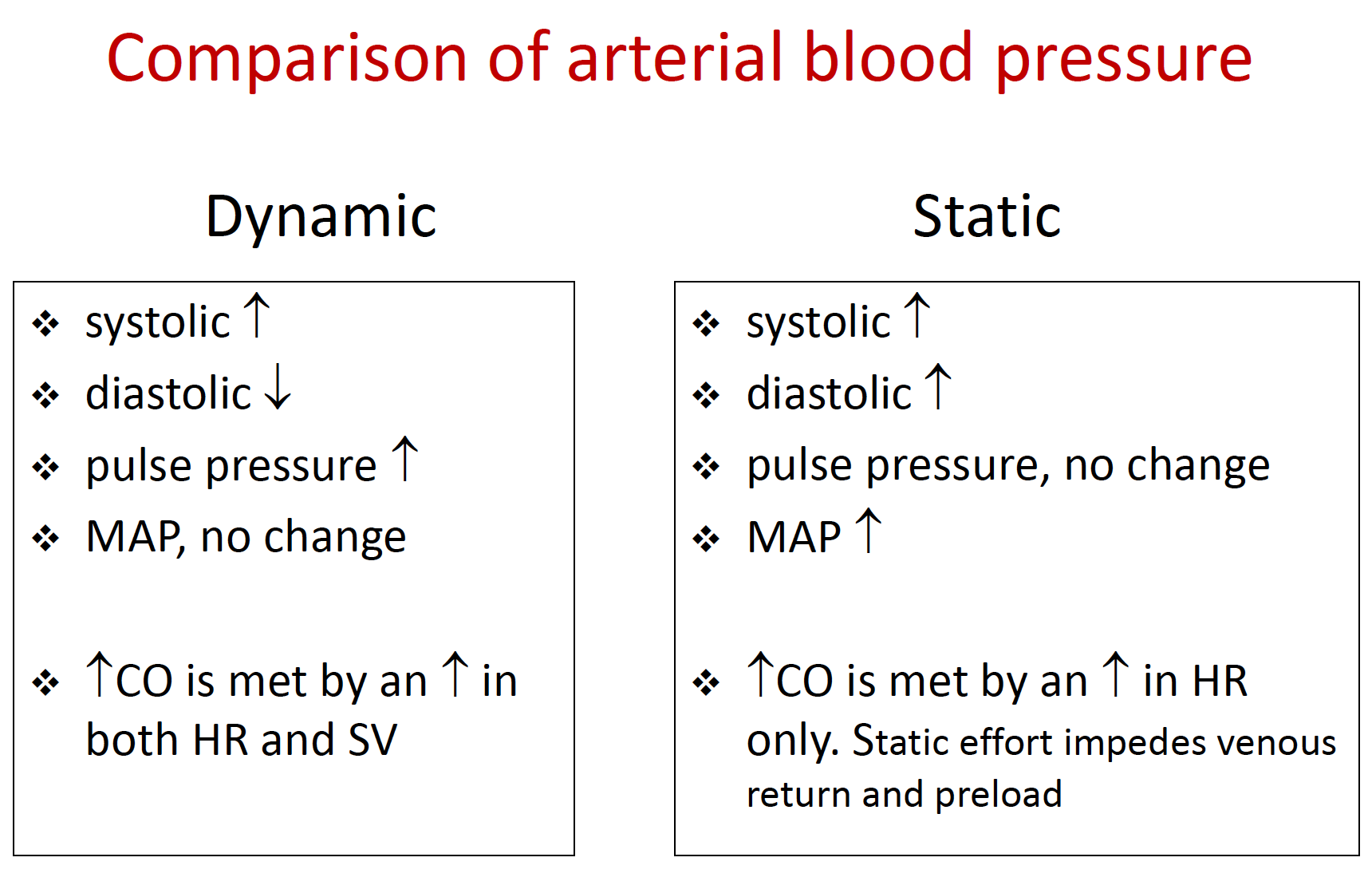
Diastolic pressure does not depend on cardiac output and will either remain the same or actually decrease. High bloodstream pressure is an important condition and often it has no symptoms. An increase in blood pressure during exercise particularly the systolic reading is normal and expected with levels that return to the usual resting range after recovery from exercise.
The increase in diastolic blood pressure during mild exercise with increasing serum cholesterol or insulin resistance is likely to be of clinical relevance. If you know your blood pressure find out. The reasons for this are as follows.
Generally speaking an increase in both the diagnostic and systolic blood pressure is a normal thing during exercise. A spike or drop in blood pressure during exercise can be a sign of a medical condition. Blocked and inelastic arteries can be caused by poor diet age genetics or lifestyle factors.
Following exercise systolic blood pressure progressively declines during an active recovery. If you have blocked or stiff arteries they may not be able to expand enough to allow for increased blood flow during exercise therefore increasing diastolic pressure.
Why Doesn T Blood Pressure Increase During Exercise Quora
 Diastolic Blood Pressure Changes During Exercise Positively
Diastolic Blood Pressure Changes During Exercise Positively
 Blood Pressure Although Blood Pressure Increases During
Blood Pressure Although Blood Pressure Increases During
 Topic 2 Exercise Physiology 2 Ppt Download
Topic 2 Exercise Physiology 2 Ppt Download
 Systolic Blood Pressure During Exercise In Subjects With Abnormal
Systolic Blood Pressure During Exercise In Subjects With Abnormal
 Learning Objectives This Chapter Presents The Acute And Chronic
Learning Objectives This Chapter Presents The Acute And Chronic
 Systolic Blood Pressure Response To Exercise Stress Test And Risk
Systolic Blood Pressure Response To Exercise Stress Test And Risk
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/systolic-and-diastolic-blood-pressure-1746075-01-4f002165f49646d08ca287995c2af55e.png) What Are Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressures
What Are Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressures